Psychological aspects include: Spelling, Writing, Mathematics, Academic fluency (speed of reading, writing, calculating) Listening comprehension, Oral expressive skills.

Children who have developmental delay, or a specific health condition which includes things like certain genetic disorders, birth defects, and hearing loss that will probably lead to a delay will undergo early intervention program. (Toddlers upto age 5).

Social Skills influence the child’s ability to establish friendships & others social relationships. Example, to build a child’s social skills, the occupational therapist may often engage the child in group therapy.

There are three, specific types of special education interventions:
⦁ Preventive Interventions: Preventive interventions are designed to prevent potential or existing problems from becoming a disability. Special education in this form seeks to either stop something from happening or reduce a condition that has been identified.
⦁ Remedial Interventions: Remedial interventions are designed to eliminate the effects of a disability. They are generally used to teach children with disabilities skills that allow them to function successfully and independently. They may be aimed at academic, social, personal, and/or vocational goals.
⦁ Compensatory Interventions: Compensatory interventions involve teaching special skills or using special devices to improve functioning. Compensatory intervention may be best identified as teaching a child to perform a task or conquer a skill in spite of a disability. It involves providing children with disabilities an asset that non-disabled children do not need. Academic fluency (speed of reading, writing, calculating) Listening comprehension Oral expressive skills

⦁ Who are unable to reach the development center on a regular basis
⦁ Who are severely challenged and cannot benefit from the regular program
For such children, an individual program is developed with clear short-term goals after an assessment of the child. Special Educators then train the parents to carry out these specific activities as per the respective programs and regular feedback and follow-up is maintained. Counsellors and special educators interact with parents, siblings and other family members to facilitate and improve the overall life of children with disabilities.
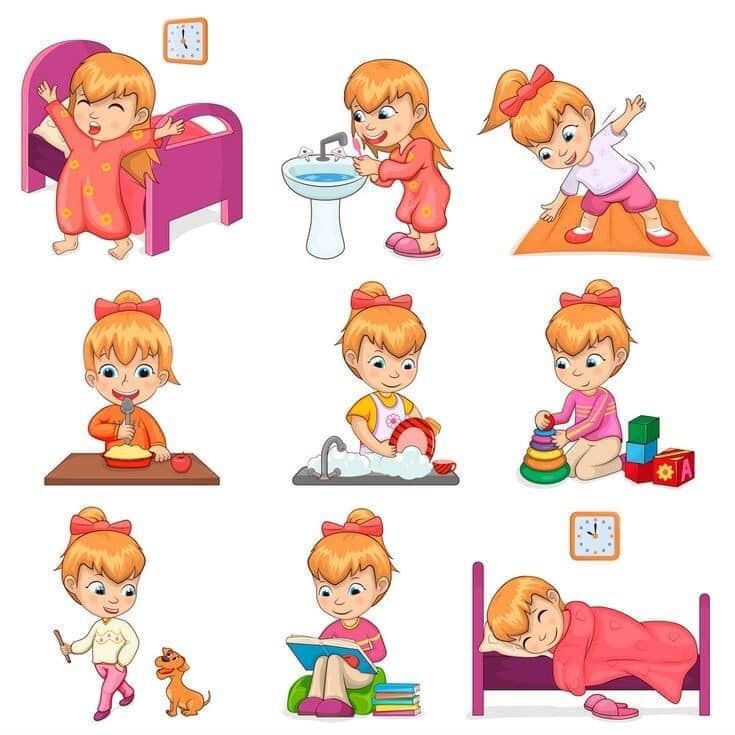

⦁ Personal hygiene:
Bathing/showering, grooming, nail care, and dental care.
⦁ Dressing:
Being able to make appropriate clothing decisions and physically dress and undress oneself.
⦁ Eating:
The ability to feed oneself, though not necessarily the capability to prepare food.
⦁Maintaining continence:
Being able to mentally and physically use a restroom. This includes the ability to get on and off the toilet and cleaning oneself.
⦁ Mobility:
Being able to stand from a sitting position, as well as get in and out of bed. The ability to walk independently from one location to another.

These include articulation therapy, language intervention activities, and others depending on the type of speech or language disorder.
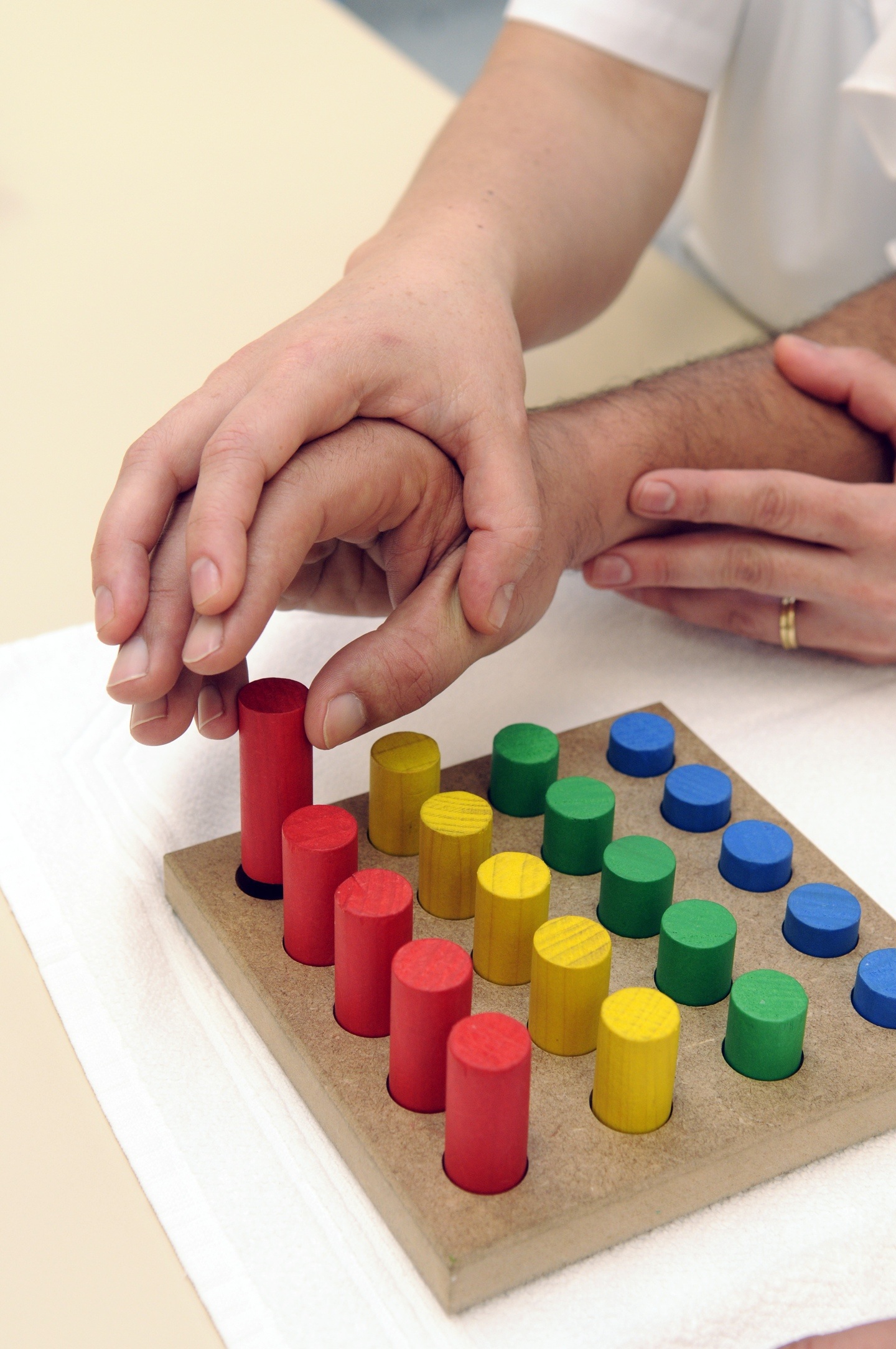



⦁ Release and exploration of emotions
⦁ Listening
⦁ Non-verbal and verbal communication
⦁ Use of both gross and fine motor movements
⦁ Sequential memory and recall of information
⦁ Self-management of behavior
⦁ Verbal discussion